Cloud Services: Navigating the Future of Online Storage and Computing
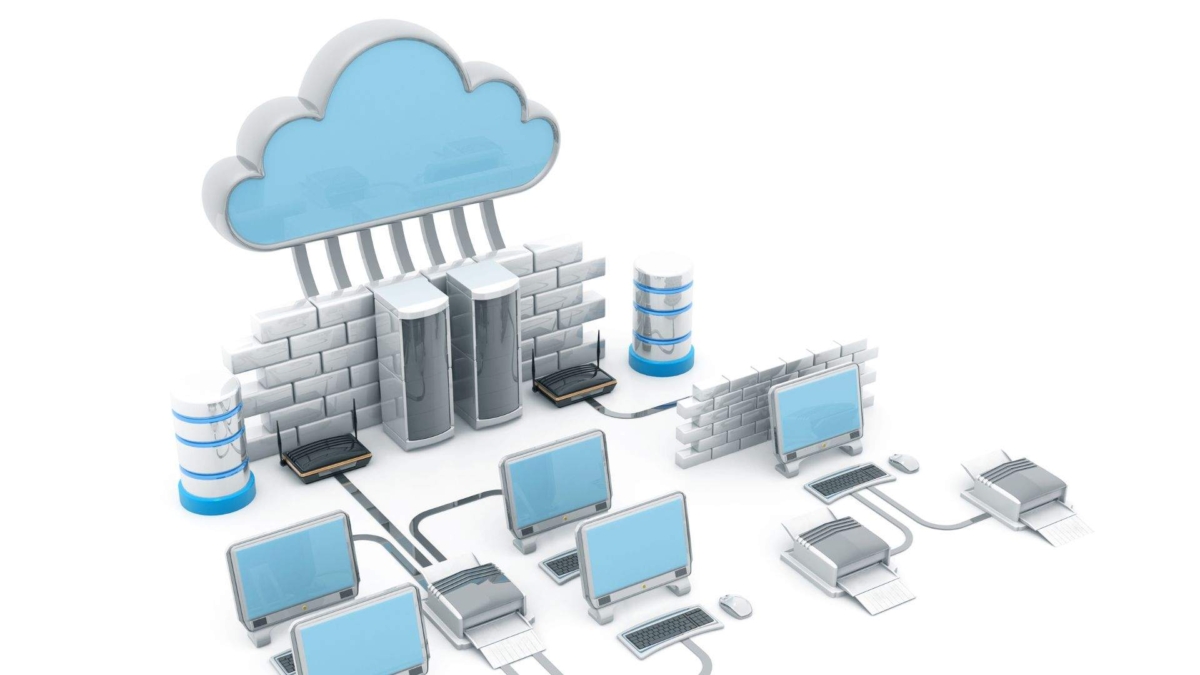
Cloud services are the delivery of computing resources over the internet, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. Cloud services allow users to access and manage data and applications without having to invest in physical infrastructure or hardware. Instead, users pay for the services they use, as they use them, and enjoy the benefits of scalability, reliability, security, and innovation.

Introduction to Cloud Services
Cloud services are a broad term that encompasses a variety of computing resources that are delivered over the internet. These resources can be anything from storage to computing power to applications. Cloud services are typically offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, which means that businesses only pay for the resources that they use. This can be a major cost saving over traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud services are not a new concept. In fact, they have been around since the early days of the Internet, when email and web hosting were some of the first examples of cloud-based applications. However, cloud services have evolved significantly over the years, thanks to the advances in technology, bandwidth, and demand. Today, cloud services offer a wide range of solutions for various needs and industries, such as:
- Online storage solutions: These are services that allow users to store and access files, photos, videos, and other data on remote servers. Examples of online storage solutions are Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive, iCloud, and Amazon S3.
- Cloud computing platforms: These are services that provide users with computing power and resources to run applications and software on demand. Examples of cloud computing platforms are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
- Software as a service (SaaS): These are services that deliver software applications over the internet, usually through a web browser or a mobile app. Users do not have to install or maintain the software on their devices. Examples of SaaS are Gmail, Netflix, Spotify, Salesforce, Zoom, and Slack.
- Platform as a service (PaaS): These are services that provide users with a platform to develop, test, deploy, and manage applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure or software. Examples of PaaS are Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, Google App Engine, and IBM Cloud Foundry.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): These are services that provide users with access to virtualized servers, storage, networks, and other hardware resources that they can configure and control as they wish. Examples of IaaS are AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), Google Compute Engine (GCE), IBM Cloud Virtual Servers (VSI), and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
In simpler terms, cloud services refer to different types of computer resources that are provided over the Internet. Companies can use these services to save money, increase their flexibility, and enhance their security measures. Cloud services provide a diverse range of options for different industries and requirements, including online storage, cloud computing platforms, SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
Benefits of Using Cloud Services
Cloud services provide numerous benefits for businesses. Firstly, they offer cost savings by allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use, eliminating the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure. Secondly, cloud services are highly scalable, enabling businesses to easily adjust their resources according to fluctuating demands. This flexibility promotes agility, allowing businesses to swiftly deploy new applications and services to adapt to market changes. Moreover, cloud providers offer robust security features that protect sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches. Additionally, cloud services provide accessibility from anywhere in the world, facilitating seamless collaboration among employees and partners regardless of their location.
Compliance features offered by cloud providers assist businesses in meeting regulatory requirements, avoiding costly fines. Furthermore, cloud providers constantly innovate, granting businesses access to cutting-edge technologies without the need for significant infrastructure investments. In summary, cloud services offer businesses the advantages of cost savings, scalability, agility, enhanced security, accessibility, compliance support, and access to the latest technologies.
Cloud services or cloud computing offer many advantages for users who want to store and process data online. Some of the main benefits are:
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud services eliminate the need for users to purchase or maintain expensive hardware or software. Users only pay for what they use and can scale up or down their usage depending on their needs. This can result in significant savings in operational and capital expenses.
- Scalability: Cloud computing can handle large amounts of data and traffic without compromising performance or quality. Users can easily add or remove resources as needed without affecting the availability or functionality of their applications. This can help users cope with changing demands and growth opportunities.
- Reliability: Cloud solutions are designed to be resilient and fault-tolerant. It has backup systems and redundancies in place to ensure that data is always accessible and secure. Users can also benefit from automatic updates and patches that keep their applications up to date and secure.
- Security: Cloud computing has advanced security measures and protocols to protect data from unauthorized access or loss. Users can also leverage encryption, authentication, authorization, firewalls, and other tools to enhance their data security and privacy. Additionally, cloud service providers comply with various regulations and standards that ensure data protection and compliance.
- Innovation: Cloud enables users to access the latest technologies and features without having to invest in research and development. Users can also leverage scalable cloud platforms to experiment with new ideas and solutions without risking their existing infrastructure or operations.
Cloud services offer a number of benefits for users who want to store and process data online. These benefits include cost-efficiency, scalability, reliability, security, compliance, and innovation. Cloud services are reliable and ensure data accessibility and security through backup systems and automatic updates. They offer enhanced security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, and they comply with regulations to ensure data protection and privacy. Cloud services also foster innovation by granting access to the latest technologies.

Security in Cloud Services
While cloud services offer many benefits for users who want to store and process data online, they also pose some challenges and risks that need to be addressed. One of the main concerns is security. Security in cloud computing refers to the protection of data from unauthorized access or loss while it is stored or transmitted over the internet.
Security in cloud services is a shared responsibility between the cloud service provider and the user. The cloud service provider is responsible for securing the physical infrastructure and network that host the cloud services. The user is responsible for securing the data and applications that they use on the cloud services.
Some of the best practices for ensuring security in cloud services are:
- Choosing a reputable cloud service provider that has a proven track record of providing reliable and secure cloud services.
- Reviewing the terms and conditions of the cloud service provider to understand their security policies and practices.
- Encrypting data before uploading it to the cloud service provider or using encryption tools provided by the cloud service provider.
- Using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to access the cloud service provider and the data stored on it.
- Implementing access control and permission policies to limit who can access or modify the data stored on the cloud service provider.
- Monitoring and auditing the activity and performance of the cloud service provider and the data stored on it.
- Backing up data regularly and keeping copies of it on different locations or devices.
- Updating and patching the applications and software that are used on the cloud service provider.
Cloud solutions are the future of online storage and computing. They offer many advantages for users who want to store and process data online, such as cost-efficiency, scalability, reliability, security, and innovation. However, they also present some challenges and risks that need to be addressed, especially in terms of security. Users need to be conscious of the security implications of using cloud solutions and take necessary measures to protect their data and applications. By doing so, they can harness the benefits of cloud-based platforms without endangering their data security or privacy.
In conclusion, cloud solutions provide a myriad of benefits for individuals and businesses seeking online data storage and processing. These advantages include cost-efficiency, scalability, reliability, security, and continuous innovation. Nonetheless, security is a paramount concern in the realm of cloud solutions, with the onus of responsibility shared between the cloud solution provider and the user. Best practices for ensuring security encompass selecting trustworthy providers, encrypting sensitive data, enforcing robust access controls, keeping a vigilant eye on activity, and performing regular data backups. By acknowledging and mitigating these challenges and risks, users can fully tap into the benefits of cloud solutions while maintaining robust data security and privacy.
Overall, cloud services represent the future of online storage and computing. They offer a transformative solution for businesses and individuals, enabling greater flexibility, cost savings, and access to cutting-edge technologies. While security considerations are important, with proper precautions and adherence to best practices, users can confidently embrace cloud solutions and unlock their full potential. Cloud services are poised to continue shaping the digital landscape, providing a robust and scalable infrastructure to meet the evolving needs of users in an increasingly interconnected world.